Ligamentum Flavum Thickening Cervical Spine | .ligamentum flavum thickening, ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, lumbar spine, degenerative disk disease, disk space height loss criteria: This specific soft tissue inflammation can be detected and documented on spinal mri studies. We describe two more cases that exhibited. Ligamentum flavum literally means yellow ligament, and is so known because it has a yellow coloring due to the amount of elastin (a springy type of collagen). In the cervical spine, the interspinous and supraspinous ligaments thicken and combine to form the nuchal ligament).
Ligamentum flavum) are paired ligaments which run between adjacent laminae of the vertebral bodies and are present relatively thin in the cervical spine, progressively becoming thickest in the lumbar spine. We speculate that repeated trivial. This tissue is similar to the type of connective tissue that comprises the other spinal ligaments, except there's a degree of elasticity to it. Major ligaments of the cervical spine. The ligamentum flavum is compromised of elastic tissue that connects the lamina from the second.
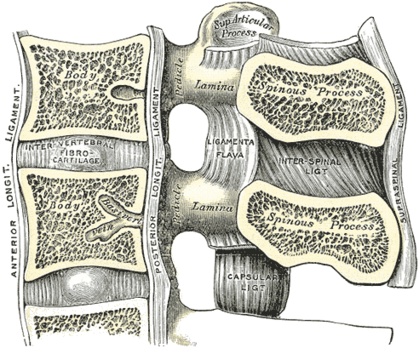
Four factors are associated with the degenerative changes of the spine that cause spinal canal stenosis: Ligamentum flavum thickening and infolding secondary to loss of disc height. Ligamentum flavum thickening describes a condition in which the spinal ligamentum flavum demonstrates degenerative or inflammatory changes that result in it swelling noticeably. Broad base along the lamina from the facet joints to base of. Assessment of traumatic brain injury online course: The ligamentum flavum limits spinal flexion (bending forward), especially abrupt flexion. The ligamentum flavum is compromised of elastic tissue that connects the lamina from the second. Ligamentum flavum literally means yellow ligament, and is so known because it has a yellow coloring due to the amount of elastin (a springy type of collagen). Complete resection of the mass that contained brownish hemorrhage was performed, resulting in excellent symptom relief. Movement of the cervical spine exacerbates congenital or acquired spinal stenosis. Related online courses on physioplus. Calcification of the ligamentum flavum can cause acute neck pain and compression of the spinal cord, which can induce myelopathy. The ligamenta flava (singular, ligamentum flavum, latin for yellow ligament) are a series of ligaments that connect the ventral parts of the laminae of adjacent vertebrae.
The yellow ligament attaches inside the. Ligamentum flavum consists of collagen fiber namely of elastin. Ligamentum flavum by dynamic disc designs corp. There have been only four cases reported in the english literature. Four days after the injury, he developed fever and his paralysis worsened.

Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy which is also known by the name of ligamentum flavum thickening is a pathological condition of the spine in which there is degeneration and swelling of the ligamentum flavum. Sakamaki t, sairyo k, sakai t, tamura t, okada y, mikami h. .ligamentum flavum thickening, ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, lumbar spine, degenerative disk disease, disk space height loss criteria: In the cervical spine, the combination of ossification of the ligamentum flavum (olf) and ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (opll) is rarely seen. Capsular ligaments form thickenings of the joint capsule and very strong to spinal flexion. The features of olf in the cervical spine were reviewed in 50 reported cases. We describe two more cases that exhibited. Thickening of the ligamentum flavum is correlated with disc degeneration and herniation 56. Although imaging protocols of the cervical spine for specific indications can vary among institutions, standard mri of the cervical spine for degenerative posterior longitudinal ligament. Assessment of traumatic brain injury online course: In hyperextension, the cervical cord increases in diameter. Ossification of ligamentum flavum (olf) mainly occurs in the thoracic spine, and rarely in the cervical spine. The supraspinous ligament (thickened in the cervical spine as the nuchal ligament), interspinous ligaments, fibrous capsules of the facet joints (which are (b) anterior view of a frontal plane section through the pedicles of the spine in which the ligamentum flavum inside the spinal canal can be seen.
Supraspinous ligament the upper cervical ligament system is especially important in stabilizing the upper cervical spine. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also known as ligamentum flavum thickening, or occasionally, as ligamentum flavum stenosis. Although imaging protocols of the cervical spine for specific indications can vary among institutions, standard mri of the cervical spine for degenerative posterior longitudinal ligament. Ossification of ligamentum flavum (olf) mainly occurs in the thoracic spine, and rarely in the cervical spine. Age, sex, location of olf, classification of olf, radiographic findings.
Unilateral ossification of the ligamentum flavum in the cervical spine with atypical radiological appearance. Sakamaki t, sairyo k, sakai t, tamura t, okada y, mikami h. The elastin pulls the ligament out of the canal when the spine is extended. Four days after the injury, he developed fever and his paralysis worsened. Thoracic spinal cord compression by ligamentum flavum ossifications. In the cervical spine, the interspinous and supraspinous ligaments thicken and combine to form the nuchal ligament). Ligamentum flavum) are paired ligaments which run between adjacent laminae of the vertebral bodies and are present relatively thin in the cervical spine, progressively becoming thickest in the lumbar spine. As we age, the ligament loses elastin. Broad base along the lamina from the facet joints to base of. The features of olf in the cervical spine were reviewed in 50 reported cases. This tissue is similar to the type of connective tissue that comprises the other spinal ligaments, except there's a degree of elasticity to it. The ligamentum flavum forms a cover over the dura mater: The ligamenta flava (singular, ligamentum flavum, latin for yellow ligament) are a series of ligaments that connect the ventral parts of the laminae of adjacent vertebrae.
It is an extremely elastic ligament, which connects the spinal bones ligamenta flava (ligamentum flavum) is thin, broad, and long in the cervical spine or the neck ligamentum flavum thickening. Ligaments of the back of the cervical and upper thoracic spine 1.
Ligamentum Flavum Thickening Cervical Spine: Broad base along the lamina from the facet joints to base of.
comment 0 Tanggapan
more_vert